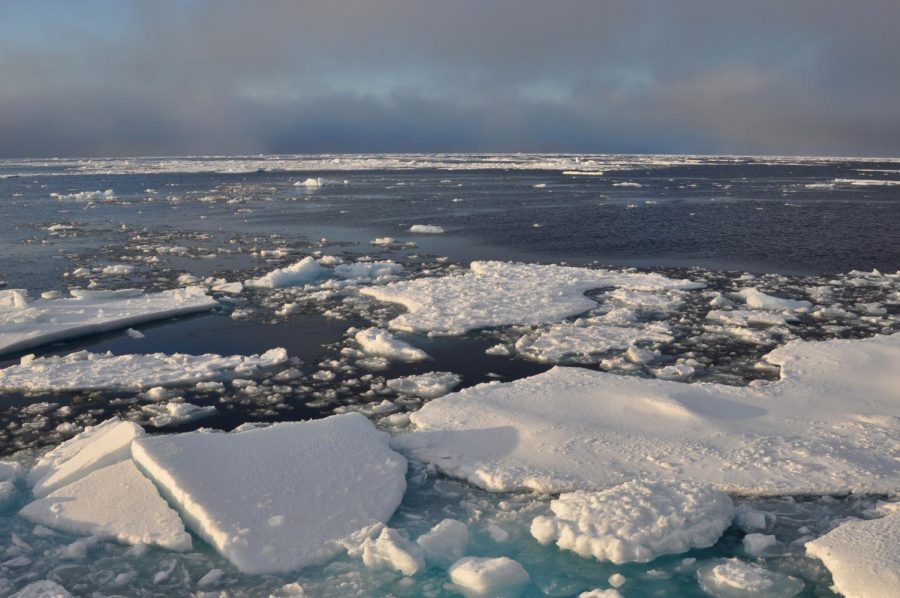
Rapid melting of Arctic Sea Ice has made its mark, according to new research, and is yet another sign of just how bad 2020 is.
An urgent report released on Sept. 15, by the U.S. The National Snow and Ice Data Data Center, showed satellites recording arctic sea ice is 3.74 m sq km (1.44 million square miles) large — the second-lowest record seen since scientists began recording it, according to European Scientist.
The sea ice sheets have been recorded since record-keeping began in the late 1970s. This year, the ice diminished at a rate similar to the 2012 lowest record, according to NASA.
The 2012 record was a result of a cyclone that broke up the remaining ice in the Arctic and shrunk it to a level of 3.41m (sq km), according to The Logical Indian.
Scientists believe the reason for this decline in ice could be due to the Siberian heat wave that was seen in spring 2020. According to NASA, sea ice started melting early and ocean levels drastically rose with temperatures reaching 14-18 degrees Fahrenheit warmer than usual.
Due to ice’s very light color, when sunlight hits its surface, the rays reflect back into the atmosphere. When ice melts, the ocean absorbs that heat instead, according to 9 News.
NASA said a recent study has shown that the Atlantic Ocean has warmer water that is rising up near the sea ice, which is ultimately warming the ice from below. Typically, warmer water from the Atlantic stays deep below Arctic waters.
With temperatures warming and ice melting, there are detrimental effects that are surging the Arctic.
Ice is vulnerable to the warming temperatures that surround it, which causes thinner ice to result, contributing to the start of the spring season, according to NASA.
This specific season absorbs more heat from the Sun which increases water temperatures because it occurs in open waters.
“As the sea ice cover extent declines, what we’re seeing is we’re continuing to lose that multilayer ice,” said Mark Serreze, director of NSIDC, according to The Logical Indian. “The ice is shrinking in the summer, but it’s also getting thinner.”
An Arctic with no ice could be seen during the late summer each year if it continues to melt at this speed. If this were to occur, it would cause a damaging hit to ocean systems.
According to The Logical Indian, Serreze discusses how seals, polar bears and phytoplankton — the foundation of the ocean’s food chain — will suffer.
When the ice melts, this will allow for dark water to be exposed, attracting and absorbing solar radiation, said 9 News.
Ice sheets in Canada and Greenland are beginning to melt due to the rising temperatures in the Arctic. According to The Logical Indian, as sheets melt in a quicker fashion, rising sea levels will increase rapidly.
“We should work very hard to make differences in our emissions of polluting gases so that we do not see so many records created in our future,” glaciologist Twila Moon told Reuters.